Important
Some information relates to prereleased product which may be substantially modified before it’s commercially released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
Want to experience Defender for Endpoint? Sign up for a free trial.
Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a capability for devices that aren’t managed by a Microsoft Endpoint Manager, either Microsoft Intune or Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, to receive security configurations for Microsoft Defender directly from Endpoint Manager.
For more information on Security Configuration Management, including prerequisites, supported platforms and more, see Manage Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Prerequisites
Review the following sections for requirements for the Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Scenario:
Environment
When a device onboards to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
- The device is surveyed for an existing Endpoint Manager presence, which is a mobile device management (MDM) enrollment to Intune
- Devices without an Endpoint Manager presence will enable the Security Management feature
- A trust is created with Azure Active Directory if one doesn’t already exist
- Azure Active Directory trust is used to communicate with Endpoint Manager (Intune) and retrieve policies
- Policy retrieve from Endpoint Manager is enforced on the device by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Active Directory Requirements
When a device that is domain joined creates a trust with Azure Active Directory, this scenario is referred to as a Hybrid Azure Active Directory Join scenario. The Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint fully supports this scenario with the following requirements:
- Azure Active Directory Connect (AAD Connect) must be synchronized to the tenant that is used from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Hybrid Azure Active Directory Join must be configured in your environment (either through Federation or AAD Connect Sync)
- AAD Connect Sync must include the device objects in scope for synchronization with Azure Active Directory (when needed for join)
- AAD Connect rules for sync must be modified for Server 2012 R2 (when support for Server 2012 R2 is needed)
- All devices must wp-signup.php in the Azure Active Directory of the tenant that hosts Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Cross-tenant scenarios are not supported.
Connectivity Requirements
Devices must have access to the following endpoints:
enterpriseregistration.windows.net– For Azure AD registration.login.microsoftonline.com– For Azure AD registration.*.dm.microsoft.com– The use of a wildcard supports the cloud-service endpoints that are used for enrollment, check-in, and reporting, and which can change as the service scales.
Supported platforms
Policies for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint security management are supported for the following device platforms:
- Windows 10 Professional/Enterprise (with KB5006738)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 with Microsoft Defender for Down-Level Devices
- Windows Server 2016 with Microsoft Defender for Down-Level Devices
- Windows Server 2019 (with KB5006744)
- Windows Server 2022 (with KB5006745)
Licensing and subscriptions
To use security management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you need:
- A subscription that grants licenses for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, like Microsoft 365, or a standalone license for only Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. For current information about options, see Minimum requirements for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Any subscription that grants Microsoft Defender for Endpoint licenses also grants your tenant access to the Endpoint security node of the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center. The Endpoint security node is where you’ll configure and deploy policies to manage Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for your devices and monitor device status.
Architecture
The following diagram is a conceptual representation of the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint security configuration management solution.
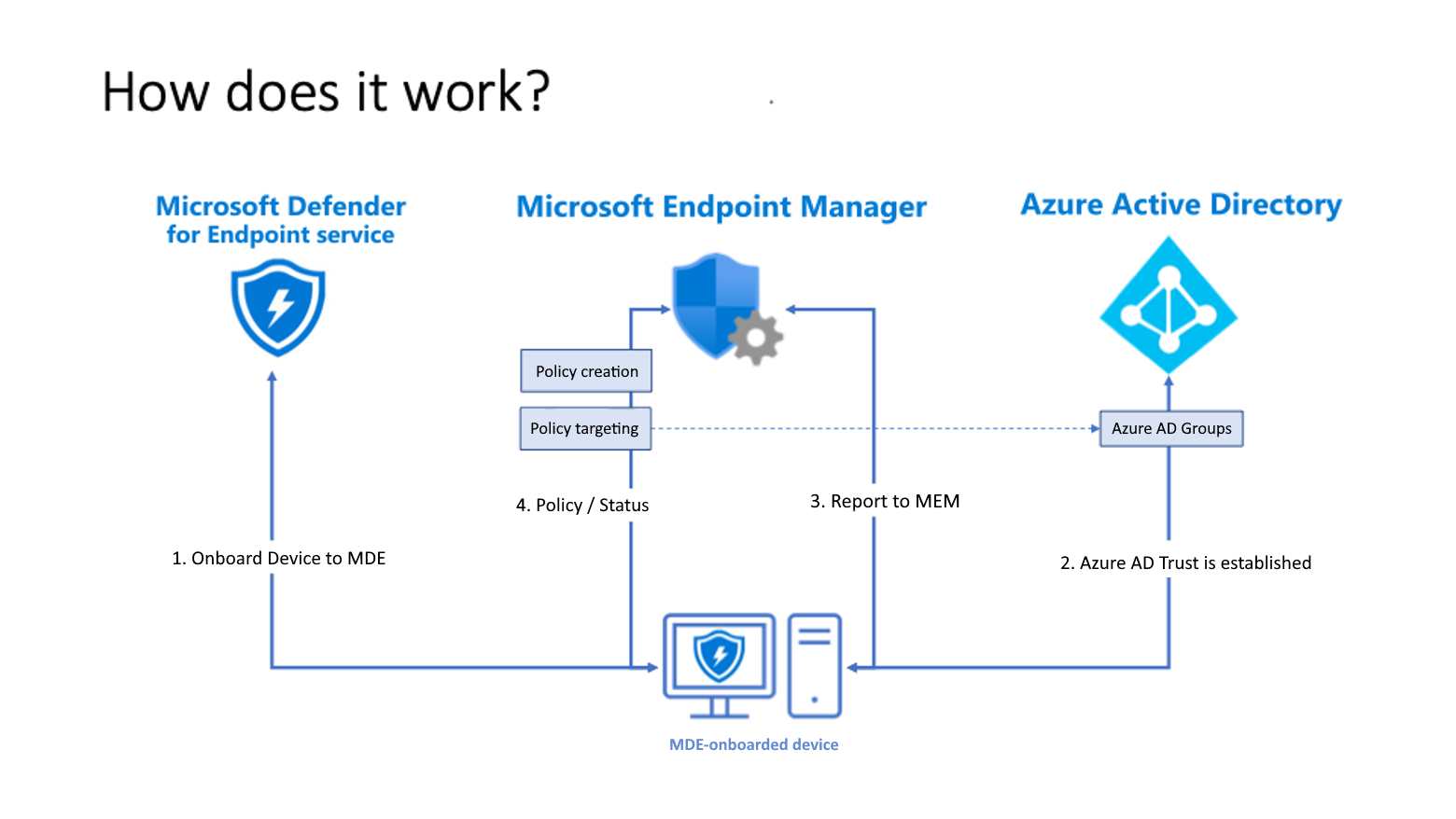
- Devices onboard to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
- A trust is established between each device and Azure AD. When a device has an existing trust, that is used. When devices haven’t wp-signup.phped, a new trust is created.
- Devices use their Azure AD Identity to communicate with Endpoint Manager. This identity enables Microsoft Endpoint Manager to distribute policies that are targeted to the devices when they check in.
- Defender for Endpoint reports the status of the policy back to Endpoint Manager.
Which solution should I use?
Microsoft Endpoint Manager includes several methods and policy types to manage the configuration of Defender for Endpoint on devices.
When your device protection needs extend beyond managing Defender for Endpoint, see Device protection overview to learn about additional capabilities provided by Microsoft Endpoint Manager to help protect devices, including device compliance, managed apps, app protection policies, and integration with third-party compliance and mobile threat defense partners.
The following table can help you understand which policies that can configure MDE settings are supported by devices that are managed by the different scenarios. When you deploy a policy that’s supported for both MDE security configuration and Microsoft Endpoint Manager, a single instance of that policy can be processed by devices that run MDE only and devices that are managed by either Intune or Configuration Manager.
| Microsoft Endpoint Manager | Workload | MDE Security configuration | Microsoft Endpoint Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint security | Antivirus |  |
 |
| Disk Encryption |  |
||
| Firewall (Profile and Rules) |  |
 |
|
| Endpoint detection and response |  |
 |
|
| Attack surface reduction |  |
||
| Account Protection |  |
||
| Device Compliance |  |
||
| Conditional Access |  |
||
| Security baselines |  |
Endpoint security policies are discrete groups of settings intended for use by security admins who focus on protecting devices in your organization.
- Antivirus policies manage the security configurations found in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. See antivirus policy for endpoint security.
- Attack surface reduction policies focus on minimizing the places where your organization is vulnerable to cyberthreats and attacks. For more information, see Overview of attack surface reduction in the Windows Threat protection documentation, and attack surface reduction policy for endpoint security.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) policies manage the Defender for Endpoint capabilities that provide advanced attack detections that are near real-time and actionable. Based on EDR configurations, security analysts can prioritize alerts effectively, gain visibility into the full scope of a breach, and take response actions to remediate threats. See endpoint detection and response policy for endpoint security.
- Firewall policies focus on the Defender firewall on your devices. See firewall policy for endpoint security.
- Firewall Rules configure granular rules for Firewalls, including specific ports, protocols, applications, and networks. See firewall policy for endpoint security.
- Security baselines include preconfigured security settings that define the Microsoft recommended security posture for different products like Defender, Edge, or Windows. The default recommendations are from the relevant product teams and enable you to quickly deploy that recommended secure configuration to devices. While settings are preconfigured in each baseline, you can create customized instances of them to establish your organization’s security expectations. See security baselines for Intune.
Configure your tenant to support Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Configuration Management
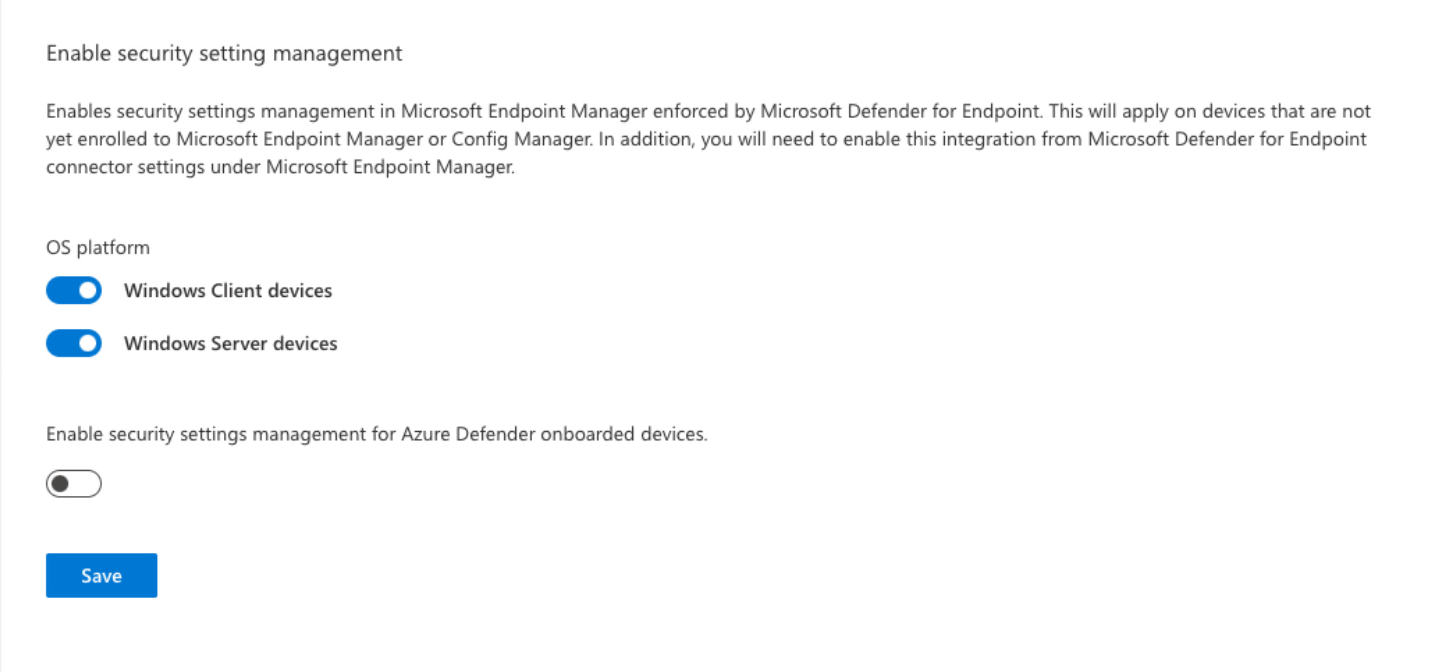
To support Microsoft Defender for Endpoint security configuration management through the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, you must enable communication between them from within each console.
- Sign in to Microsoft 365 Defender portal and go to Settings > Endpoints > Configuration Management > Enforcement Scope and enable the platforms for security settings management:
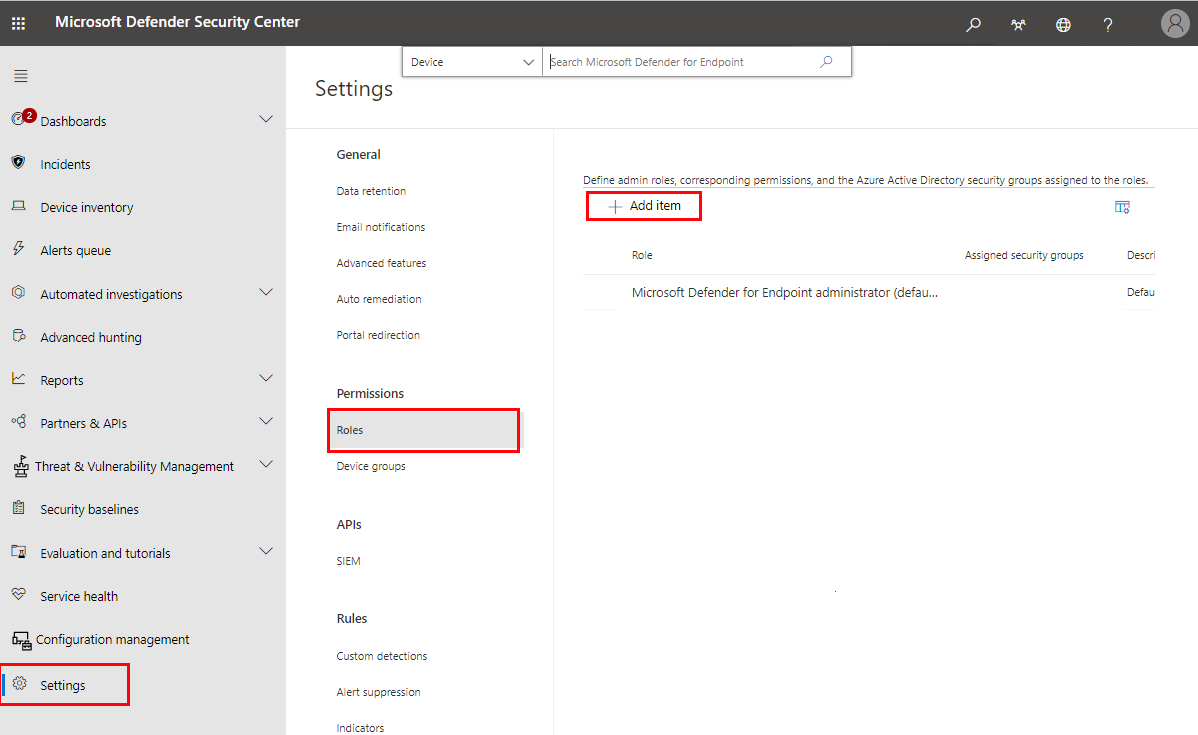
- Make sure the relevant users have permissions to manage endpoint security settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager or grant those permissions by configuring a role in the Defender portal. Go to Settings > Roles > Add item:
Tip
You can modify existing roles and add the necessary permissions versus creating additional roles in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
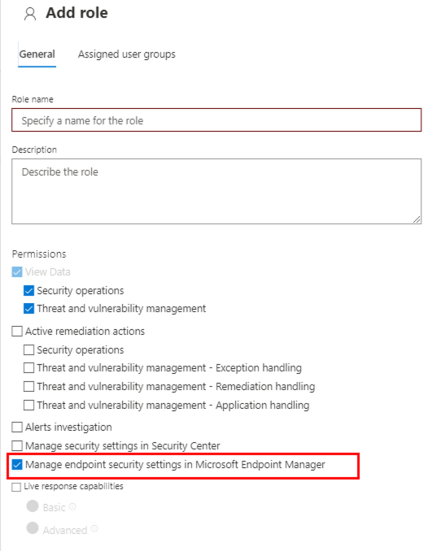
- When configuring the role, add users and be sure to select Manage endpoint security settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Select Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, and set Allow Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enforce Endpoint Security Configurations (Preview) to On.
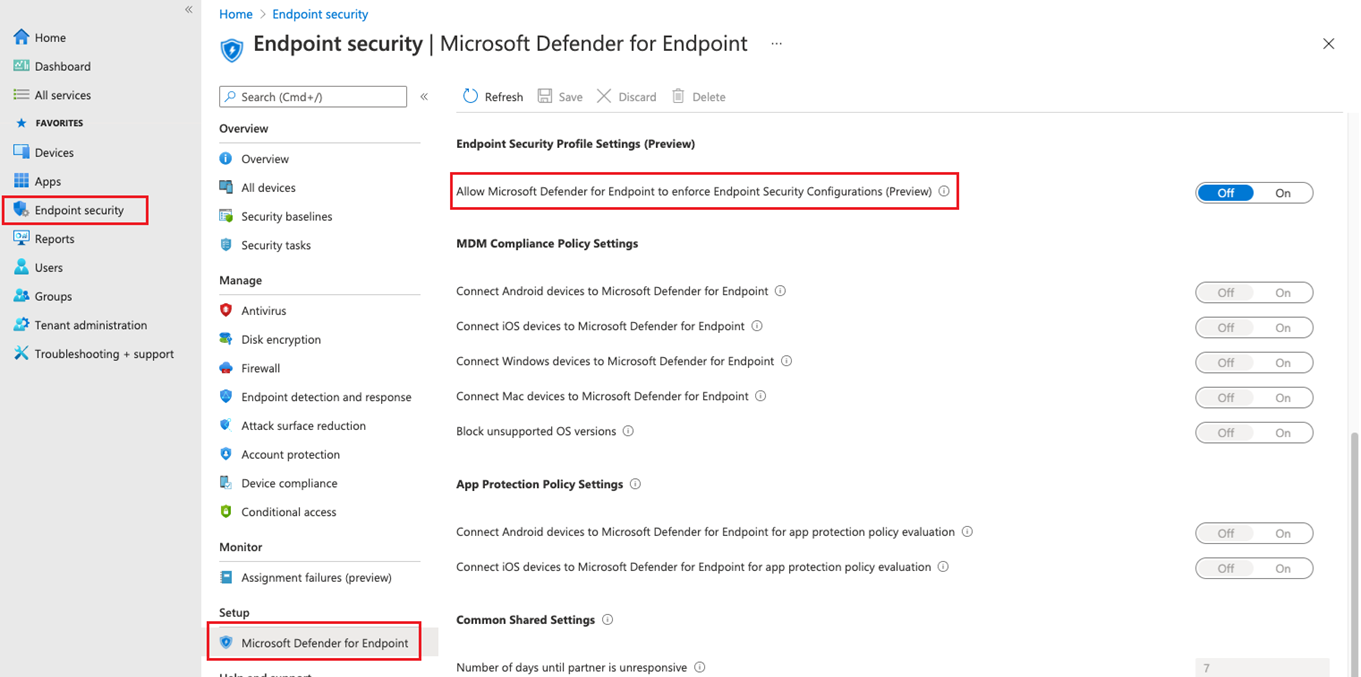
When you set this option to On, all devices in the platform scope in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint that aren’t managed by Microsoft Endpoint Manager will qualify to onboard to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Onboard devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint supports several options to onboard devices. For current guidance, see Onboarding tools and methods for Windows devices in the Defender for Endpoint documentation.
Important
After a device onboards with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, it must and be tagged with MDE-Management before it can enroll with Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. For more information on device tagging in MDE, see Create and manage device tags.
Co-existence with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
When using Configuration Manager, the best path for management of security policy is using the Configuration Manager tenant attach. In some environments it may be desired to use Security Management for Microsoft Defender. When using Security Management for Microsoft Defender with Configuration Manager, endpoint security policy should be isolated to a single control plane. Controlling policy through both channels will create the opportunity for conflicts and undesired results.
Create Azure AD Groups
After devices onboard to Defender for Endpoint, you’ll need to create device groups to support deployment of policy for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
To identify devices that have enrolled with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint but aren’t managed by Intune or Configuration Manager:
- Sign in to Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Go to Devices > All devices, and then select the column Managed by to sort the view of devices.
Devices that onboard to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and have wp-signup.phped but aren’t managed by Intune display Microsoft Defender for Endpoint in the Managed by column. These are the devices that can receive policy for security management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
You’ll also find two labels for devices that are using security management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
- MDEJoined – Added to devices that are joined to the directory as part of this scenario.
- MDEManaged – Added to devices that are actively using the security management scenario. This tag is removed from the device if Defender for Endpoint stops managing the security configuration.
You can create groups for these devices in Azure AD or from within the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
Deploy policy
After creating one or more Azure AD groups that contain devices managed by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you can create and deploy the following policies for Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to those groups:
- Antivirus
- Firewall
- Firewall Rules
- Endpoint Detection and Response
Tip
Avoid deploying multiple policies that manage the same setting to a device.
Microsoft Endpoint Manager supports deploying multiple instances of each endpoint security policy type to the same device, with each policy instance being received by the device separately. Therefore, a device might receive separate configurations for the same setting from different policies, which results in a conflict. Some settings (like Antivirus Exclusions) will merge on the client and apply successfully.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Go to Endpoint security and then select the type of policy you want to configure, either Antivirus or Firewall, and then select Create Policy.
- Enter the following properties or the policy type you selected:
- For Antivirus policy, select:
- Platform: Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server (Preview)
- Profile: Microsoft Defender Antivirus (Preview)
- For Firewall policy, select:
- Platform: Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server (Preview)
- Profile: Microsoft Defender Firewall (Preview)
- For Firewall Rules policy, select:
- Platform: Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server (Preview)
- Profile: Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules (Preview)
- For Endpoint Detection and Response policy, select:
- Platform: Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server (Preview)
- Profile: Endpoint detection and response (Preview)
Note
These profiles apply to both devices communicating through Mobile Device Management (MDM) with Microsoft Intune as well as devices that are communicating using the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint client.
Ensure you review your targeting and groups as necessary.
- For Antivirus policy, select:
- Select Create.
- On the Basics page, enter a name and description for the profile, then choose Next.
- On the Configuration settings page, select the settings you want to manage with this profile. To learn more about a setting, expand its information dialog and select the Learn more link to view the CSP information for the setting in the on-line documentation.
When your done configuring settings, select Next.
- On the Assignments page, select the Azure AD groups that will receive this profile. For more information on assigning profiles, see Assign user and device profiles.
Select Next to continue.
Tip
- Assignment filters are not supported for Security Configuration Management profiles.
- Only Device Objects are applicable for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint management. Targeting users is not supported.
- Policies configured will apply to both Microsoft Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint clients
- Complete the policy creation process and then on the Review + create page, select Create. The new profile is displayed in the list when you select the policy type for the profile you created.
- Wait for the policy to be assigned and view a success indication that policy was applied.
- You can validate that settings have applied locally on the client by using the Get-MpPreference command utility.
Note
This capability is being rolled out gradually.
For more information on Security Configuration Management, see Manage Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
If you encounter enrollment issues, see Troubleshoot Security Configuration Management onboarding issues.
Note
This capability does not apply to devices that are already enrolled to Microsoft Endpoint Manager (either Intune or Configuration Manager). Devices enrolled into Intune will continue to receive policies through their established management channel.
Identify onboarded devices
Use the following steps to validate that your endpoints have successfully completed the Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint onboarding process.
- Verify that the device appears in the Device Inventory section of Microsoft 365 Defender.
- In the Azure Active Directory portal, verify that the device has successfully been enrolled.
- In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager Admin Center, verify that the device has successfully been enrolled by looking it up in the Devices > All devices section.
Offboard devices
To offboard devices that have been onboarded via Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, see Offboard devices from the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint service.
Note
Offboarding will disable Tamper Protection if it is enabled.

