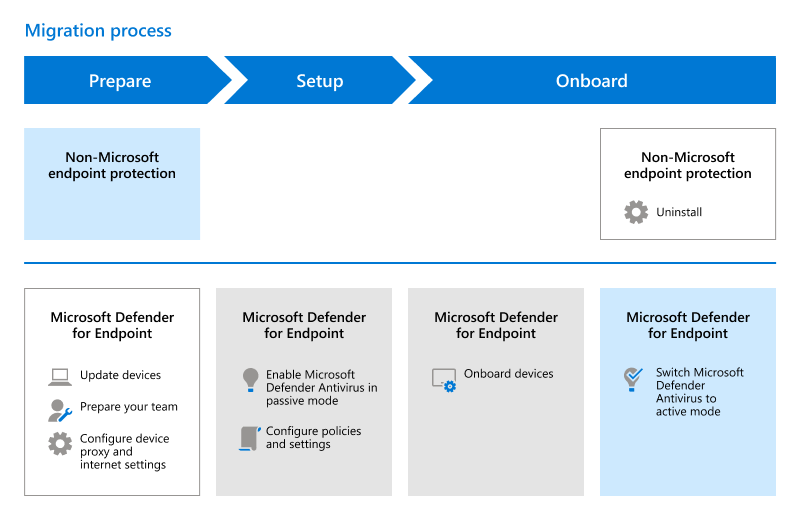
When you make the switch to Defender for Endpoint, you begin with your non-Microsoft antivirus/antimalware protection in active mode. Then, you configure Microsoft Defender Antivirus in passive mode, and onboard your devices to Defender for Endpoint. Next, you configure your endpoint protection features, set Microsoft Defender Antivirus to active mode, and verify that everything is working correctly. Finally, you remove the non-Microsoft solution.
The migration process
The process of migrating to Defender for Endpoint can be divided into three phases, as described in the following table:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Prepare for your migration | During the Prepare phase: 1. Update your organization’s devices. 2. Get Defender for Endpoint. 3. Plan roles and permissions, and grant access to the Microsoft 365 Defender portal. 4. Configure your device proxy and internet settings to enable communication between your organization’s devices and Defender for Endpoint. |
| Set up Defender for Endpoint | During the Setup phase: 1. Enable/reinstall Microsoft Defender Antivirus, and set it to passive mode. 2. Configure Defender for Endpoint. 3. Add Defender for Endpoint to the exclusion list for your existing solution. 4. Add your existing solution to the exclusion list for Microsoft Defender Antivirus. 5. Set up your device groups, collections, and organizational units. 6. Configure your antimalware policies and real-time protection settings. |
| Onboard to Defender for Endpoint | During the Onboard phase: 1. Onboard your devices to Defender for Endpoint. 2. Run a detection test. 3. Confirm that Microsoft Defender Antivirus is running in passive mode. 4. Get updates for Microsoft Defender Antivirus. 5. Uninstall your existing endpoint protection solution. 6. Make sure that Defender for Endpoint working correctly. |
What’s included in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint?
In this migration guide, we focus on next-generation protection and endpoint detection and response capabilities as a starting point for moving to Defender for Endpoint. However, Defender for Endpoint includes much more than antivirus and endpoint protection. Defender for Endpoint is a unified platform for preventative protection, post-breach detection, automated investigation, and response. The following table summarizes features and capabilities in Defender for Endpoint.
| Feature/Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Threat & vulnerability management | Threat & vulnerability management capabilities help identify, assess, and remediate weaknesses across your endpoints (such as devices). |
| Attack surface reduction | Attack surface reduction rules help protect your organization’s devices and applications from cyberthreats and attacks. |
| Next-generation protection | Next-generation protection includes Microsoft Defender Antivirus to help block threats and malware. |
| Endpoint detection and response | Endpoint detection and response capabilities detect, investigate, and respond to intrusion attempts and active breaches. |
| Advanced hunting | Advanced hunting capabilities enable your security operations team to locate indicators and entities of known or potential threats. |
| Behavioral blocking and containment | Behavioral blocking and containment capabilities help identify and stop threats, based on their behaviors and process trees even when the threat has started execution. |
| Automated investigation and remediation | Automated investigation and response capabilities examine alerts and take immediate remediation action to resolve breaches. |
| Threat hunting service (Microsoft Threat Experts) | Threat hunting services provide security operations teams with expert level monitoring and analysis, and to help ensure that critical threats aren’t missed. |

