Live response gives security operations teams instantaneous access to a device (also referred to as a machine) using a remote shell connection. This gives you the power to do in-depth investigative work and take immediate response actions to promptly contain identified threats in real time.
Live response is designed to enhance investigations by enabling your security operations team to collect forensic data, run scripts, send suspicious entities for analysis, remediate threats, and proactively hunt for emerging threats.
With live response, analysts can do all of the following tasks:
- Run basic and advanced commands to do investigative work on a device.
- Download files such as malware samples and outcomes of PowerShell scripts.
- Download files in the background (new!).
- Upload a PowerShell script or executable to the library and run it on a device from a tenant level.
- Take or undo remediation actions.
Before you begin
Before you can initiate a session on a device, make sure you fulfill the following requirements:
- Verify that you’re running a supported version of Windows.
Devices must be running one of the following versions of Windows
- Windows 10 & 11
- Version 1909 or later
- Version 1903 with KB4515384
- Version 1809 (RS 5) with with KB4537818
- Version 1803 (RS 4) with KB4537795
- Version 1709 (RS 3) with KB4537816
- macOS – Only applicable for Public Preview, minimum required version: 101.43.84
- Linux – Only applicable for Public Preview, minimum required version: 101.45.13
- Windows Server 2012 R2 – with KB5005292
- Windows Server 2016 – with KB5005292
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows 10 & 11
- Enable live response from the advanced settings page.
You’ll need to enable the live response capability in the Advanced features settings page.
Note
Only users with manage security or global admin roles can edit these settings.
- Enable live response for servers from the advanced settings page (recommended).
Note
Only users with manage security or global admin roles can edit these settings.
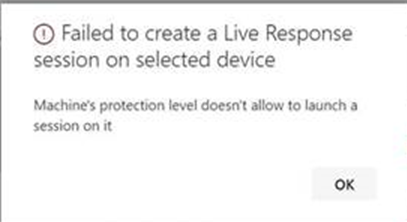
- Ensure that the device has an Automation Remediation level assigned to it.
You’ll need to enable, at least, the minimum Remediation Level for a given Device Group. Otherwise you won’t be able to establish a Live Response session to a member of that group.
You’ll receive the following error:
- Enable live response unsigned script execution (optional).
Important
Signature verification only applies for PowerShell scripts.
Warning
Allowing the use of unsigned scripts may increase your exposure to threats.
Running unsigned scripts is not recommended as it can increase your exposure to threats. If you must use them however, you’ll need to enable the setting in the Advanced features settings page.
- Ensure that you have the appropriate permissions.
Only users who have been provisioned with the appropriate permissions can initiate a session. For more information on role assignments, see Create and manage roles.
Important
The option to upload a file to the library is only available to users with with “Manage Security Settings” permission. The button is greyed out for users with only delegated permissions.
Depending on the role that’s been granted to you, you can run basic or advanced live response commands. Users permissions are controlled by RBAC custom role.
Live response dashboard overview
When you initiate a live response session on a device, a dashboard opens. The dashboard provides information about the session such as the following:
- Who created the session
- When the session started
- The duration of the session
The dashboard also gives you access to:
- Disconnect session
- Upload files to the library
- Command console
- Command log
Initiate a live response session on a device
- Sign in to Microsoft 365 Defender portal.
- Navigate to Endpoints > Device inventory and select a device to investigate. The devices page opens.
- Launch the live response session by selecting Initiate live response session. A command console is displayed. Wait while the session connects to the device.
- Use the built-in commands to do investigative work. For more information, see Live response commands.
- After completing your investigation, select Disconnect session, then select Confirm.
Live response commands
Depending on the role that’s been granted to you, you can run basic or advanced live response commands. User permissions are controlled by RBAC custom roles. For more information on role assignments, see Create and manage roles.
Note
Live response is a cloud-based interactive shell, as such, specific command experience may vary in response time depending on network quality and system load between the end user and the target device.
Basic commands
The following commands are available for user roles that are granted the ability to run basic live response commands. For more information on role assignments, see Create and manage roles.
| Command | Description | Windows and Windows Server | macOS | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd | Changes the current directory. | Y | Y | Y |
| cls | Clears the console screen. | Y | Y | Y |
| connect | Initiates a live response session to the device. | Y | Y | Y |
| connections | Shows all the active connections. | Y | N | N |
| dir | Shows a list of files and subdirectories in a directory. | Y | Y | Y |
| drivers | Shows all drivers installed on the device. | Y | N | N |
fg <command ID> |
Place the specified job in the foreground in the foreground, making it the current job. NOTE: fg takes a ‘command ID` available from jobs, not a PID | Y | Y | Y |
| fileinfo | Get information about a file. | Y | Y | Y |
| findfile | Locates files by a given name on the device. | Y | Y | Y |
| getfile <file_path> | Downloads a file. | Y | Y | Y |
| help | Provides help information for live response commands. | Y | Y | Y |
| jobs | Shows currently running jobs, their ID and status. | Y | Y | Y |
| persistence | Shows all known persistence methods on the device. | Y | N | N |
| processes | Shows all processes running on the device. | Y | Y | Y |
| registry | Shows registry values. | Y | N | N |
| scheduledtasks | Shows all scheduled tasks on the device. | Y | N | N |
| services | Shows all services on the device. | Y | N | N |
| trace | Sets the terminal’s logging mode to debug. | Y | Y | Y |
Advanced commands
The following commands are available for user roles that are granted the ability to run advanced live response commands. For more information on role assignments, see Create and manage roles.
| Command | Description | Windows and Windows Server | macOS | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| analyze | Analyses the entity with various incrimination engines to reach a verdict. | Y | N | N |
| collect | Collects forensics package from machine | N | Y | Y |
| isolate | Disconnects the device from the network while retaining connectivity to the Defender for Endpoint service | N | Y | N |
| release | Releases a device from network isolation | N | Y | N |
| run | Runs a PowerShell script from the library on the device. | Y | Y | Y |
| library | Lists files that were uploaded to the live response library. | Y | Y | Y |
| putfile | Puts a file from the library to the device. Files are saved in a working folder and are deleted when the device restarts by default. | Y | Y | Y |
| remediate | Remediates an entity on the device. The remediation action will vary depending on the entity type: File: delete Process: stop, delete image file Service: stop, delete image file Registry entry: delete Scheduled task: remove Startup folder item: delete file NOTE: This command has a prerequisite command. You can use the -auto command in conjunction with remediate to automatically run the prerequisite command. | Y | Y | Y |
| scan | Disconnects the device from the network while retaining connectivity to the Defender for Endpoint service | N | Y | Y |
| undo | Restores an entity that was remediated. | Y | Y | Y |
Use live response commands
The commands that you can use in the console follow similar principles as Windows Commands.
The advanced commands offer a more robust set of actions that allow you to take more powerful actions such as download and upload a file, run scripts on the device, and take remediation actions on an entity.
Get a file from the device
For scenarios when you’d like get a file from a device you’re investigating, you can use the getfile command. This allows you to save the file from the device for further investigation.
Note
The following file size limits apply:
getfilelimit: 3 GBfileinfolimit: 10 GBlibrarylimit: 250 MB
Download a file in the background
To enable your security operations team to continue investigating an impacted device, files can now be downloaded in the background.
- To download a file in the background, in the live response command console, type
download <file_path> &. - If you are waiting for a file to be downloaded, you can move it to the background by using Ctrl + Z.
- To bring a file download to the foreground, in the live response command console, type
fg <command_id>.
Here are some examples:
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
getfile "C:\windows\some_file.exe" & |
Starts downloading a file named some_file.exe in the background. |
fg 1234 |
Returns a download with command ID 1234 to the foreground. |
Put a file in the library
Live response has a library where you can put files into. The library stores files (such as scripts) that can be run in a live response session at the tenant level.
Live response allows PowerShell scripts to run, however you must first put the files into the library before you can run them.
You can have a collection of PowerShell scripts that can run on devices that you initiate live response sessions with.
To upload a file in the library
- Click Upload file to library.
- Click Browse and select the file.
- Provide a brief description.
- Specify if you’d like to overwrite a file with the same name.
- If you’d like to be, know what parameters are needed for the script, select the script parameters check box. In the text field, enter an example and a description.
- Click Confirm.
- (Optional) To verify that the file was uploaded to the library, run the
librarycommand.
Cancel a command
Anytime during a session, you can cancel a command by pressing CTRL + C.
Warning
Using this shortcut will not stop the command in the agent side. It will only cancel the command in the portal. So, changing operations such as “remediate” may continue, while the command is canceled.
Run a script
Before you can run a PowerShell/Bash scripts, you must first upload it to the library.
After uploading the script to the library, use the run command to run the script.
If you plan to use an unsigned PowerShell script in the session, you’ll need to enable the setting in the Advanced features settings page.
Warning
Allowing the use of unsigned scripts may increase your exposure to threats.
Apply command parameters
- View the console help to learn about command parameters. To learn about an individual command, run:
PowerShell
help <command name> - When applying parameters to commands, note that parameters are handled based on a fixed order:
PowerShell
<command name> param1 param2 - When specifying parameters outside of the fixed order, specify the name of the parameter with a hyphen before providing the value:
PowerShell
<command name> -param2_name param2 - When using commands that have prerequisite commands, you can use flags:
PowerShell
<command name> -type file -id <file path> - autoor
PowerShellremediate file <file path> - auto`
Supported output types
Live response supports table and JSON format output types. For each command, there’s a default output behavior. You can modify the output in your preferred output format using the following commands:
-output json-output table
Note
Fewer fields are shown in table format due to the limited space. To see more details in the output, you can use the JSON output command so that more details are shown.
Supported output pipes
Live response supports output piping to CLI and file. CLI is the default output behavior. You can pipe the output to a file using the following command: [command] > [filename].txt.
Example:
processes > output.txt
View the command log
Select the Command log tab to see the commands used on the device during a session. Each command is tracked with full details such as:
- ID
- Command line
- Duration
- Status and input or output side bar
Limitations
- Live response sessions are limited to 25 live response sessions at a time.
- Live response session inactive timeout value is 30 minutes.
- Getfile command inactive timeout value is 30 minutes. It is considered inactive while the command is running in the background.
- A user can initiate up to 10 concurrent sessions.
- A device can only be in one session at a time.
- The following file size limits apply:
getfilelimit: 3 GBfileinfolimit: 10 GBlibrarylimit: 250 MB

